Introduction
Classic Hodgkin's lymphoma (cHL) is a highly curable lymphoid malignancy. Most of the patients receive either bleomycin or brentuximab vedotin (BV) based therapies as a frontline treatment. Treatment alterations are common and can be related to toxicity, patient's preference, and/or clinical evidence of response. The aim of our study is to explore the frequency and characteristics of treatment alterations, especially bleomycin and BV, in frontline therapies used in newly diagnosed cHL.
Methods
This single center study included patients with a diagnosis of cHL who were first seen at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center between January 1,2016 and May 28, 2020 for either newly diagnosed cHL or relapsed/refractory (R/R) cHL.
Patients' charts were reviewed to assess frequency of treatment discontinuation at the time of frontline therapy and underlying reasons for any treatment alterations. The primary aims were to assess the frequency of treatment alterations and its effects on overall survival (OS), and progression-free survival (PFS). Descriptive statistics including mean, standard deviation, median, and range for continuous variables such as age, and lab measurements, and frequency counts and percentages for categorical variables such as race, gender, and response were analyzed. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for time-to-event analysis including PFS and OS. Median time to event in months with 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated. The Log-rank test was used to evaluate the difference in time-to-event endpoints between patient groups. Statistical software SAS 9.4 (SAS, Cary, NC) and S-Plus 8.2 (TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA) were used for statistical analyses.
Results
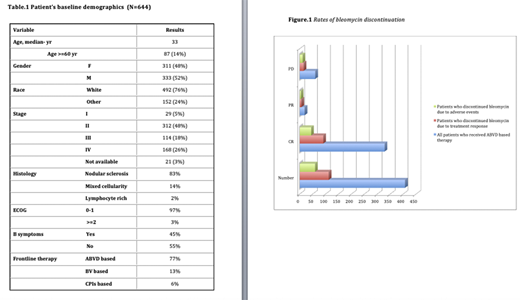
In the studied period, 644 patients met the inclusion criteria. The median age at diagnosis was 33 years (range:9-85) with 52% males. Advanced stage (stages III and IV) occurred in 45% of patients. Ninety-seven percent of patients had 0-1 Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status. Histological subtype was predominately nodular sclerosis (83%). International prognostic index at the time of diagnosis was ≥4 in 13% of patients. Most of the patients received doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine and dacarbazine (ABVD) based therapy (77%). Other therapies included brentuximab vedotin (BV)(13%) and checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) (6%, as a part of clinical trial). Patient's demographics are outlined in Table.1. Treatment alteration, which included either addition or omission of drug/s, occurred in 26% of patients. The most common discontinued drugs were bleomycin (79%), and BV (15%). Of the patients who were started on ABVD based therapy, the frequency of bleomycin discontinuation was 26% (116 of 455 patients). The most common reasons for bleomycin discontinuation were: treatment response as per the RATHL study (49%), pulmonary toxicity (27%) and other treatment-related toxicity (9%). Of the patients who were started on frontline BV based therapy, the frequency of BV discontinuation was 26% (20 of 78 patients). The most common reasons for BV discontinuation were: peripheral neuropathy (65%), skin rash (10%) and other treatment-related toxicity (25%). Patients who discontinued bleomycin due to adverse events (AEs) had a higher chance of primary refractory disease at the end of frontline treatment (19% vs. 15%, p-value: 0.005) while patients who discontinued bleomycin due to treatment response had similar rates of primary refractory disease (13% vs. 15%, p-value: 0.57). The median cycles number of bleomycin based therapy were the same (6 cycles) among all the groups (those who continued bleomycin without AEs or discontinuation, patients who discontinued bleomycin for treatment response and patients who discontinued bleomycin for AEs) . Patients who discontinued BV due to AEs had similar outcome to the patients who continued the treatment without alterations.
Conclusions
Frontline treatment alterations in cHL are common. Positron emission tomography treatment response based bleomycin discontinuation was not associated with worse PFS or OS. However bleomycin discontinuation secondary to AEs was associated with a statistically significant higher rate of primary refractory disease and subsequent worse PFS and OS. BV discontinuation secondary to AEs didn't result in worse outcomes.
Parmar:Cellenkos Inc.:Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding.Iyer:CRISPR:Research Funding;Spectrum:Research Funding;Merck:Research Funding;Afffimed:Research Funding;Rhizen:Research Funding;Seattle Genetics, Inc.:Research Funding;Legend Biotech:Consultancy;Daiichi Sankyo:Consultancy;Trillium:Research Funding;Curio Biosciences:Honoraria;Target Oncology:Honoraria.Nieto:Affimed:Consultancy, Other: Grant Support;Novartis:Other: Grant Support;Secura Bio:Other: Grant Support;Astra Zeneca:Other: Grant Support.Chuang:Sage-Evidence=Based Medicine & Practice:Consultancy.Wang:Lu Daopei Medical Group:Honoraria;Pulse Biosciences:Consultancy;Molecular Templates:Research Funding;BioInvent:Research Funding;VelosBio:Research Funding;Beijing Medical Award Foundation:Honoraria;Juno:Consultancy, Research Funding;Oncternal:Consultancy, Research Funding;AstraZeneca:Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses, Research Funding;Celgene:Consultancy, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses, Research Funding;InnoCare:Consultancy;Loxo Oncology:Consultancy, Research Funding;Verastem:Research Funding;Acerta Pharma:Research Funding;Pharmacyclics:Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses, Research Funding;Janssen:Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses, Research Funding;MoreHealth:Consultancy;OncLive:Honoraria;Kite Pharma:Consultancy, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses, Research Funding;Nobel Insights:Consultancy;Guidepoint Global:Consultancy;Dava Oncology:Honoraria;OMI:Honoraria, Other: Travel, accommodation, expenses;Targeted Oncology:Honoraria.Lee:Celgene:Research Funding;Guidepoint Blogal:Consultancy;Bristol-Myers Squibb:Consultancy, Research Funding;Aptitude Health:Speakers Bureau;Oncternal Therapeutics:Research Funding;Seattle Genetics:Research Funding;Takeda:Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal